top of page
Shop by test name, symptom or disease
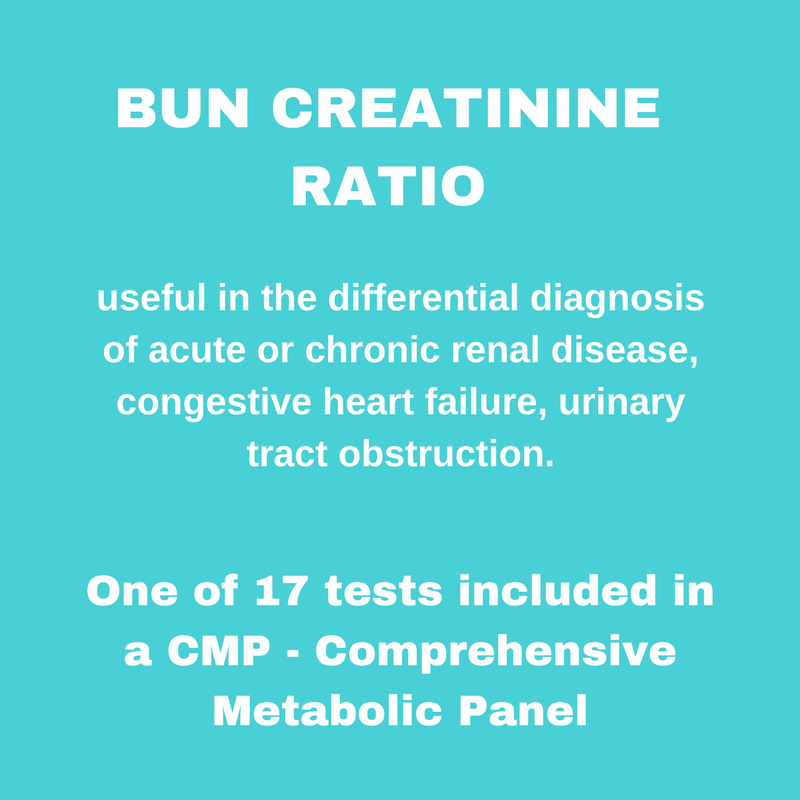
BUN/CREATININE RATIO
$21.00
On Sale
was
$99.00
Save 79%
In stock
Save this product for later
BUN/CREATININE RATIO
Product Details
Clinical Significance
The BUN/Creatinine ratio is useful in the differential diagnosis of acute or chronic renal disease. Reduced renal perfusion, e.g., congestive heart failure, or recent onset of urinary tract obstruction will result in an increase in BUN/Creatinine ratio. Increased urea formation also results in an increase in the ratio, e.g., gastrointestinal bleeding, trauma, etc. When there is decreased formation of urea as seen in liver disease, there is a decrease in the BUN/Creatinine ratio. In most cases of chronic renal disease the ratio remains relatively normal.
Alternative Name(s)
BUN, Blood Urea Nitrogen
Reference Range(s)
| Bun/Creatinine Ratio | 6-22 (calc) | ||||
| Urea Nitrogen (BUN) | |||||
| Age | Male (mg/dL) | Female (mg/dL) | |||
| <1 Month | 4-12 | 3-17 | |||
| 1-11 Months | 2-13 | 4-14 | |||
| 1-3 Years | 3-12 | 3-14 | |||
| 4-19 Years | 7-20 | 7-20 | |||
| ≥20 Years | 7-25 | 7-25 | |||
| Creatinine | ||
| Age | Male (mg/dL) | Female (mg/dL) |
| 18-19 years | 0.60-1.26 | 0.50-1.00 |
| 20-49 years | 0.60-1.35 | 0.50-1.10 |
| 50-59 years | 0.70-1.33 | 0.50-1.05 |
| 60-69 years | 0.70-1.25 | 0.50-0.99 |
| 70-79 years | 0.70-1.18 | 0.60-0.93 |
| ≥80 years | 0.70-1.11 | 0.60-0.88 |
| eGFR Non-African American | ≥60 mL/min/1.73m2 |
| eGFR African American | ≥60 mL/min/1.73m2 |
Test Prep: None Indicated
Display prices in:
USD
bottom of page